Procedural Animation
- CPU Animator
- GPU Animator
The default animation processing path is to use animation clips to drive animated bone poses. Procedural animation is another approach to moving skeletal bone poses according to certain mathematical algorithms.
Such algorithms should be implemented as systems that run within the AnimationInjectionSystemGroup.
Dynamic Bone Chain

The dynamic bone chain is a simulation system that applies spring-based physics, smoothing, and blending to transform hierarchies.
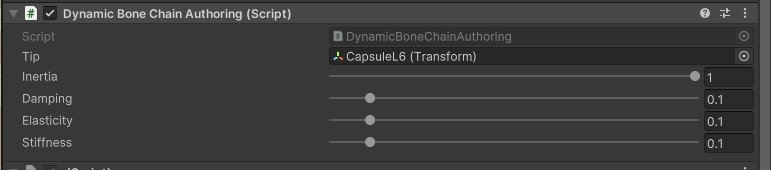
The authoring script must be placed on the root bone of the simulated hierarchy. The following parameters can be configured:
- Tip - the end bone of the simulated bone chain.
- Damping - controls how quickly a dynamic bone’s oscillations lose energy, preventing endless wobbling by reducing velocity each frame.
- Elasticity - determines how strongly a dynamic bone tries to return to its rest position, acting like the stiffness of a spring.
- Stiffness - controls how rigidly a dynamic bone resists bending, keeping it closer to its original orientation instead of freely swaying.
The dynamic bone chain consists of one component and one buffer:
public struct DynamicBoneChainComponent: IComponentData, IEnableableComponent
{
public float inertia;
public float damping;
public float elasticity;
public float stiffness;
public float timeAccumulator;
public float3 prevPosition;
}
public struct DynamicBoneChainNode: IBufferElementData
{
public int parentIndex;
public float3 position;
public float3 prevPosition;
public BoneTransform referenceLocalPose;
public Entity boneEntity;
}
Unsupported
Procedural animations are not supported by GPU Animator.