Shaders with Deformations
For the correct rendering of skinned meshes deformed by Rukhanka, a deformation-aware shader should be created.
To make this task Unity Shader Graph, Amplify Shader Editor, or Better Shaders tool can be used.
Simple deformation-compatible shaders can be found in Rukhanka samples
Unity Shader Graph
Creating deformation-compatible shaders using Unity Shader Graph is straightforward:
-
Create a shader graph (URP or HDRP depending on the render pipeline you are using) and open it for editing.
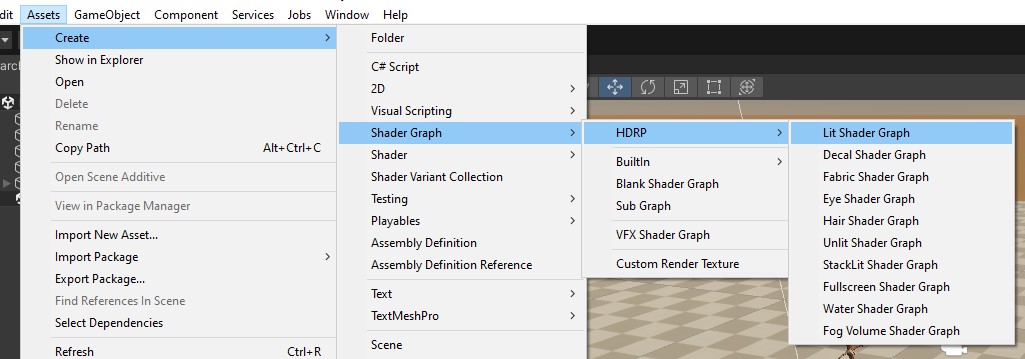
-
Navigate to the
Packages/Rukhanka Animation System 2/Rukhanka.Editor/ShaderGraph/folder in the project inspector window.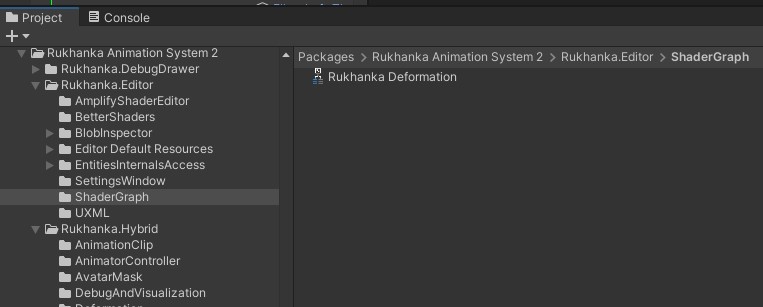
-
Add
Rukhanka Deformationsubgraph to the createdShaderGraphby dragging and dropping it from the project inspector. -
Connect position, normal, and tangent output ports of the
Rukhanka Deformationnode to the corresponding input ports of the master node.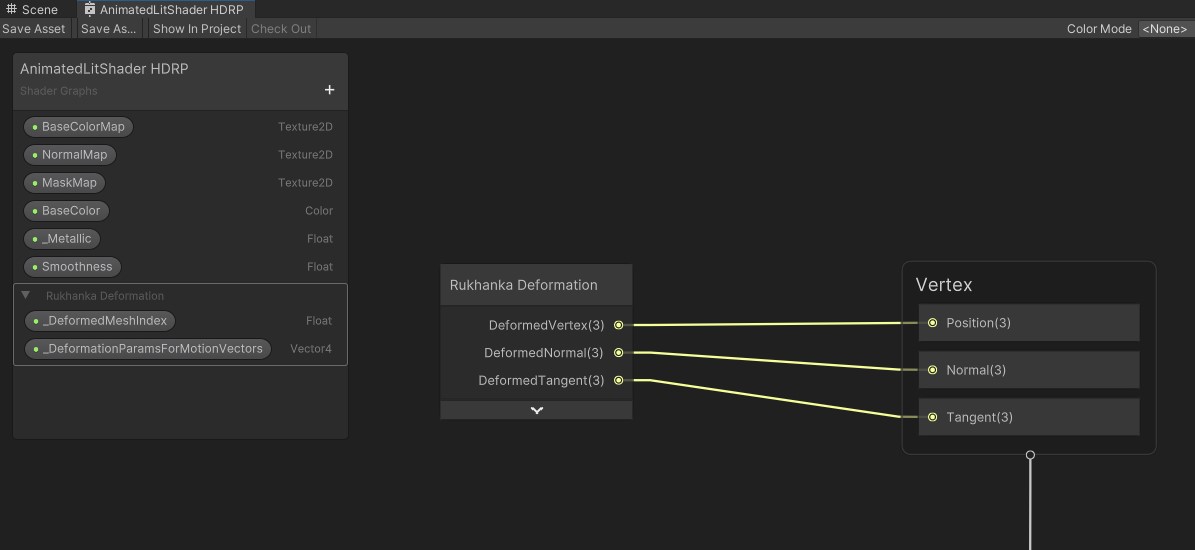
-
Create two shader parameters:
-
_DeformedMeshIndexwith typefloat. -
_DeformationParamsForMotionVectorswith typeVector4.Make both parameters declared as
Hybrid Per Instance.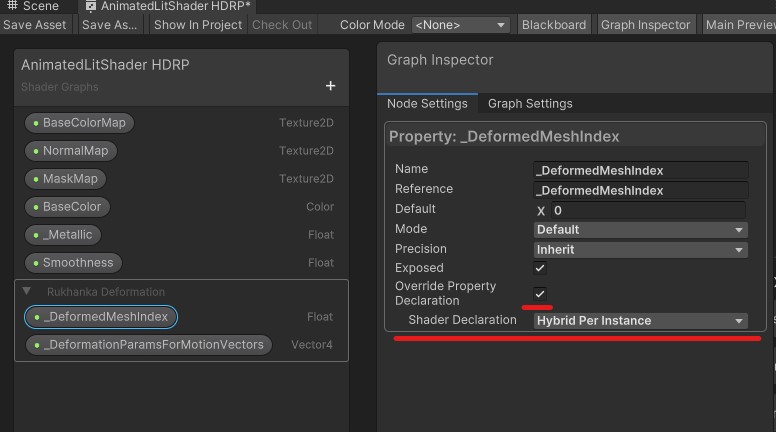
- Save and assign this newly created shader to the materials of skinned mesh renderers.
Production Ready Shaders included in the Shader Graph sample assets can be used as animated shader templates
Amplify Shader Editor
The process of creating deformation aware shader in Amplify Shader Editor is also simple:
-
Create
Amplify Shaderand open it for editing.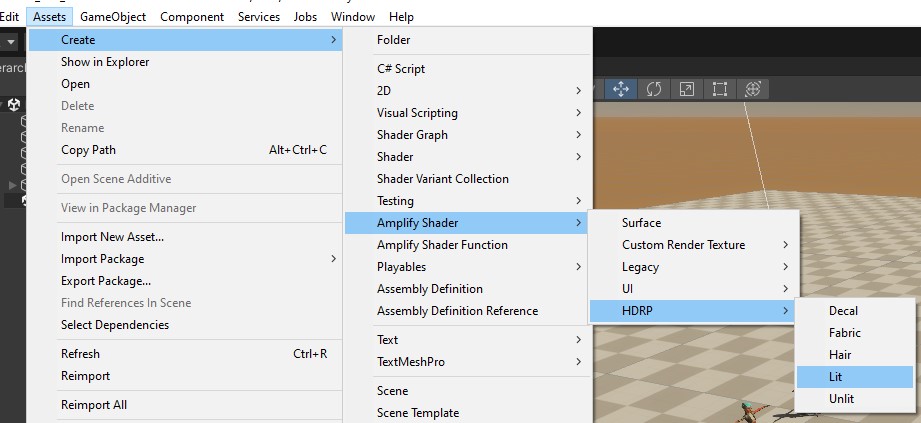
-
Navigate to the
Packages/Rukhanka Animation System 2/Rukhanka.Editor/AmplifyShaderEditor/folder in the project inspector window.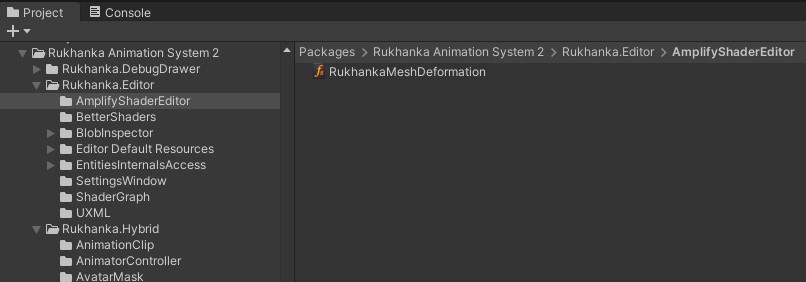
-
Add
RukhankaMeshDeformationamplify shader function to the created shader by dragging and dropping it from the project inspector. -
Connect the vertex position, normal, and tangent output ports of the
Rukhanka Mesh Deformationnode to the corresponding input ports of the master node. -
Set vertex position mode of the master node to
Absolute.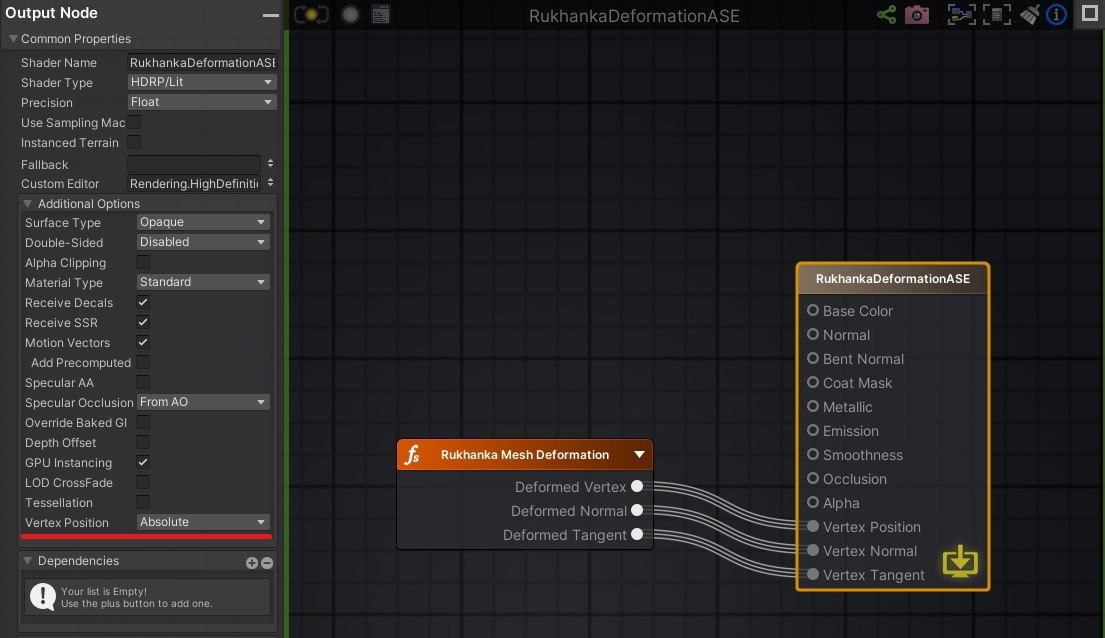
-
Save and assign this newly created shader to the materials of skinned mesh renderers.
Better Shaders
The Better Shaders is a source-based shader generation tool. Rukhanka provides the shader snippets that can be included in your BetterShaders shader.
Navigate to the Rukhanka installation directory and copy Rukhanka.Editor/BetterShaders/StackableRukhankaDeformation.surfshader and Rukhanka.Editor/BetterShaders/StackableRukhankaDeformationMotionVectors.surfshader files to the directory with your BetterShaders shader. Use StackableRukhankaDeformation.surfshader or StackableRukhankaDeformationMotionVectors.surfshader (depending on motion vector requirements) in the first line of BEGIN_SUBSHADERS/END_SUBSHADERS block. An example of a lit shader can be as follows:
BEGIN_OPTIONS
Stackable "False"
ShaderName "BetterShaders/LitAnimated"
END_OPTIONS
BEGIN_SUBSHADERS
// Must be first line in subshader list
"StackableRukhankaDeformation.surfshader"
// Use this line instead if RUKHANKA_ENABLE_DEFORMATION_MOTION_VECTORS script symbol is defined
//"StackableRukhankaDeformationMotionVectors.surfshader"
"Lit.surfshader"
END_SUBSHADERS
Direct Source Code Modification
The shader source code can be modified to properly work with Rukhanka deformations. The process can be described as follows:
Shader Properties Section
Define the following two shader variables:
[HideInInspector]_DeformedMeshIndex("Deformed Mesh Buffer Index Offset", Float) = 0
[HideInInspector]_DeformationParamsForMotionVectors("Deformation Parameters", Float) = 0
For each pass
1. Enable the DOTS instancing variant
#pragma multi_compile _ DOTS_INSTANCING_ON
2. Add variables to the UnityPerMaterial constant buffer
Find or create the UnityPerMaterial constant buffer declaration and add both variables:
CBUFFER_START(UnityPerMaterial)
float _DeformedMeshIndex;
float4 _DeformationParamsForMotionVectors;
CBUFFER_END
3. Add variables to the UserPropertyMetadata DOTS instancing section
Find or create the UserPropertyMetadata DOTS instancing props section and add both variables:
#ifdef UNITY_DOTS_INSTANCING_ENABLED
UNITY_DOTS_INSTANCING_START(UserPropertyMetadata)
UNITY_DOTS_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _DeformedMeshIndex)
UNITY_DOTS_INSTANCED_PROP(float4, _DeformationParamsForMotionVectors)
UNITY_DOTS_INSTANCING_END(UserPropertyMetadata)
#endif
4. Include the deformation compute file after the UserPropertyMetadata section:
#include "Packages/com.rukhanka.animation/Rukhanka.Runtime/Deformation/Resources/ComputeDeformedVertex.hlsl"
5. Modify vertex shader input structure. Add a vertexID field with the SV_VertexID semantic:
struct Attributes
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
float4 tangent : TANGENT;
float4 texcoord0 : TEXCOORD0;
uint vertexID : SV_VertexID;
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};
6. Modify vertex shader entry function. At the beginning of the vertex shader entry function, add a call to ComputeDeformedVertex_float:
Varyings LitPassVertex(Attributes input)
{
Varyings output = (Varyings)0;
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
UNITY_TRANSFER_INSTANCE_ID(input, output);
UNITY_INITIALIZE_VERTEX_OUTPUT_STEREO(output);
// It is important to place this function right after builtin 'instanceID' initialization
ComputeDeformedVertex_float(input.vertexID, input.vertex.xyz, input.normal.xyz, input.tangent.xyz,
input.vertex.xyz, input.normal.xyz, input.tangent.xyz);
...
}
If the vertex attribute structure does not include normal or tangent members, replace them with dummy variables defined before calling ComputeDeformedVertex_float:
struct MinimalAttributes
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
uint vertexID : SV_VertexID;
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};
Varyings ShadowPassVertex(MinimalAttributes input)
{
Varyings output = (Varyings)0;
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
UNITY_TRANSFER_INSTANCE_ID(input, output);
UNITY_INITIALIZE_VERTEX_OUTPUT_STEREO(output);
float3 unusedNormal = 0;
float3 unusedTangent = 0;
ComputeDeformedVertex_float(input.vertexID, input.vertex.xyz, unusedNormal, unusedTangent,
input.vertex.xyz, unusedNormal, unusedTanent);
...
}
Third-Party Shaders
Rukhanka Technologies can help you adapt custom shaders to work with Rukhanka Animation. Please contact us by support email or the official Discord server.